In my previous post I blogged about open source frameworks for mobile end-to-end testing and in the other past post I described about how to setup the Greenhouse sample app environment.
In this post I would like to describe how to test an Android app with Calabash-Android, which was open sourced in the beginning of March.
The basic architecture of Calabash is described in this figure, which I have taken from the Less Painful homepage:
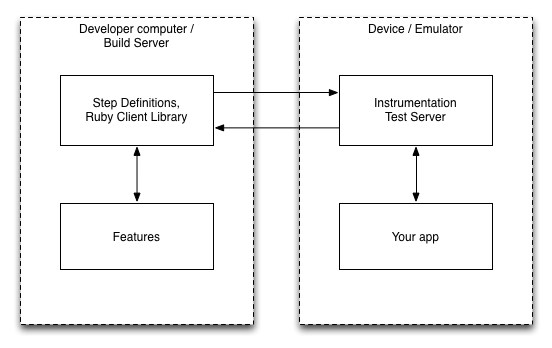
From an architectural perspective there is a client, that it using Cucumber by default, that is sending command to a server, that is running on the device/emulator, and that is used to communicate with the application under test (AUT) using the Robotium framework. The communication between the client and the server is done using a socket connection sending Json commands. Going with this approach the AUT doesn’t need to be modified (e.g. server to be added) because in the Android test project this remote server is added. Using the Robotium framework is a good choice, because it is the defacto standard for automated Android end-to-end testing. From my perspective adding this extra remote component makes sense, because in the real world you probably have to create before running the test some test data that you will use in your test. Without having this remote architecture you need to add all the helpers that are communicating with the test system (using various protocols) to you test apk.
To get started to test the Greenhouse Android app, you need first to clone the Calabash-Android project from Github:
git clone git://github.com/calabash/calabash-android.git
git submodule init
git submodule update
Now you need to compile the Greenhouse Android app using the “mvn clean install” command and copy the greenhouse.apk file from the target folder into the base folder of the Calabash Android project. If you would like to run the Greenhouse app on a device, you need to modify the the property base.url in the file dev.properties to the IP where your Greenhouse server app is running.
To configure Calabash please update the build.properties file like this:
tested.package_name=com.springsource.greenhouse
tested.main_activity=com.springsource.greenhouse.MainActivity
tested.project.apk=greenhouse.apk
Now you can execute the tests on an emulator (please make sure this is started before) running the command:
ant clean test
All details about this setup you find as well in the first screencast:
Writing tests is pretty simple, there are predefined steps.
My added steps can be found in the ddary_steps.rb file. The interesting part about the test is, that the first part of the test is testing a webview (authorization of the app) and the second part is using Android native UI elements. The elements in the webview are identified using css locators.
All details about the test execution can be found in the second part of the screencast:
Adding new command to Calabash-android is pretty easy. All commands, that you can use in your Ruby code, are mapped to Actions:
sh.calaba.instrumentationbackend.actions
The command press_button_with_text is implemented in the class PressButtonText. The method key() is used for mapping the class to the command name and the execute(..) method is used to talk to the Robotium solo object. New written actions are only available if they are located in this package: sh.calaba.instrumentationbackend.actions